SNAPSHOTS
Viewing any information within VpK requires the application to connect to a snapshot of Kubernetes information.
Two methods exist to create a VpK Snapshot. These are:
- From a local VpK installation connect to a running K8s cluster
- From a running VpK Docker container ssh to host machine and connect to a running K8s cluster
NOTE: Both above options require the user to have connected to a running cluster with the kubectl CLI (or other CLI tool) prior to using VpK. VpK will issue the kubectl command (or other command) with the needed parameters to query the K8s cluster and obtain the data to create the snapshot.
A validated connection to the Kubernetes cluster must be established outside of VpK. VpK will not obtain data from the cluster if a valid kubectl connection does not exist.
Once a valid connection has been established with a Kubernetes cluster VpK can be used to create the snapshot. VpK will invoke a series of commands that will obtain information from the running cluster.
The following table provides the command, output file name if one is created, and a brief description.
| Command | Output file | Description |
|---|---|---|
| kubectl version | version.json | The version of the K8s cluster and client. |
| kubectl get --raw="/readyz?verbose" | readyz.json | Ready status of resources in the cluster. |
| kubectl cluster-info dump | components.json | Parsed output from the command to located components in the cluster. |
| kubectl api-resources -o wide | n/a | A list of all defined resource kinds in the cluster. Information is parsed and the kind and namespaced data is used with the get command. |
| kubectl get <kind> -n <namespace> -o json | vpk.snapshot.json | A single file with all string formatted output from the get commands. The <kind> and <namespace> values are obtained from the parsed output from the api-resources command. |
| kubectl explain <kind> | version.json | The explain information for each resource located in the cluster. |
Local machine running VpK
The following diagram is an overview of when VpK has been installed locally with npm and running as a node.js application. The VpK server component communicates with the K8s cluster using the kubectl command CLI.
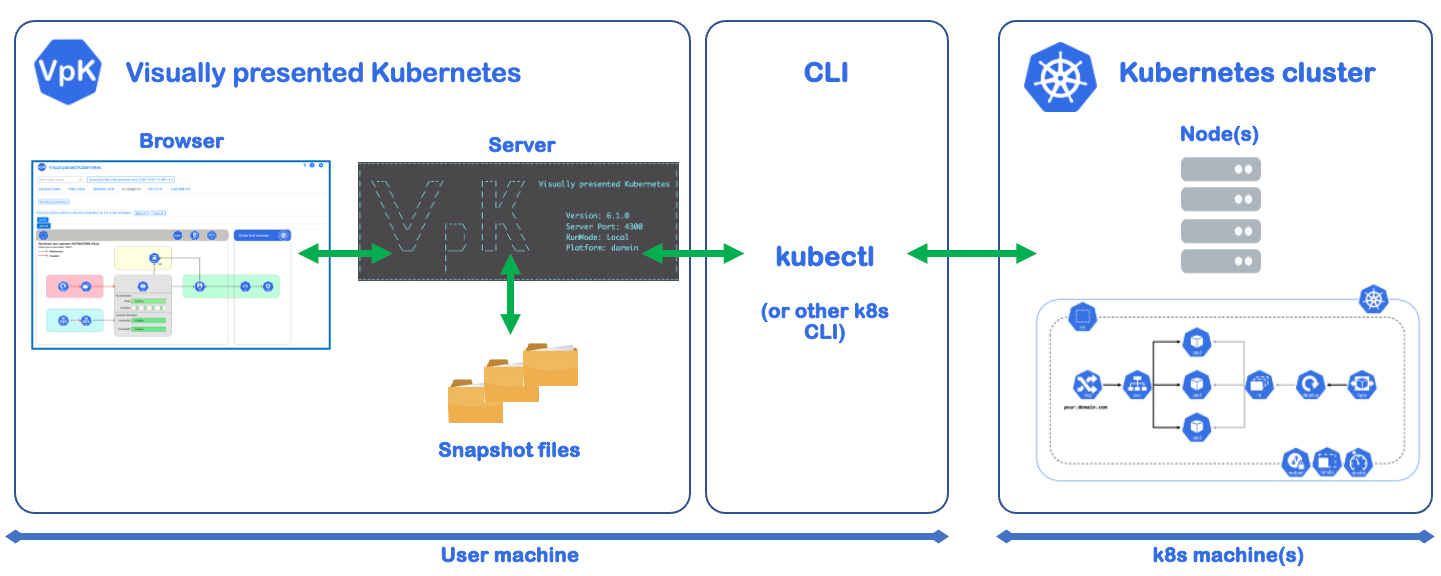
The above diagram depicts the Kubernetes cluster as not running on the same machine as VpK. This does not have to be the case when minikube, kind, or other like solutions are used. When using those solutions to host the K8s cluster VpK will obtain information from the cluster that is running on the same machine as VpK.
Docker container running VpK
The following diagram is an overview of when the docker container for VpK is running. The VpK server communicates with the kubectl command CLI to query the K8s cluster from the Docker container to the local host via SSH.
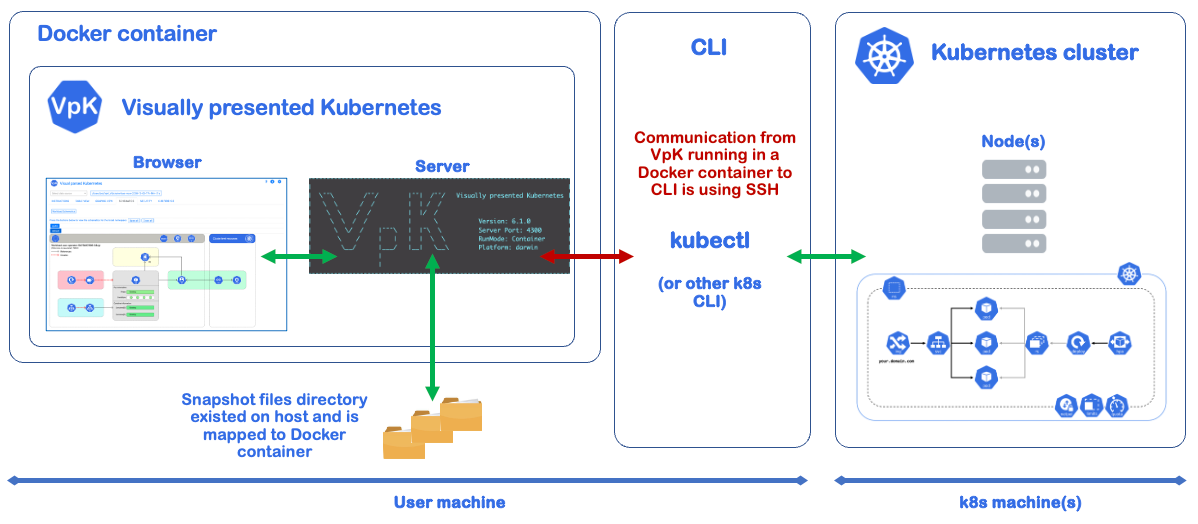
Create a snapshot
A snapshot is required to view any of the K8s resources. Creation of a new snapshot or connecting to an existing snapshot should be the first task any time the application is started.
At the top of the screen from drop-down box select the desired option to create a new snapshot or use and existing snapshot.
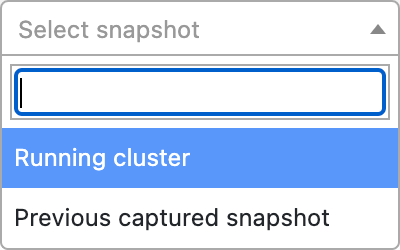
Drop-down when running VpK locally
When running VpK locally the drop has two options as shown below.
The first option, Running cluster, requires a kubectl or other CLI be connected to an existing Kubernetes cluster. Use of this option will run a series of kubectl commands to obtain the information from the cluster and create a new snapshot. Once the new snapshot is created the data will be parsed and the UI will be updated with the information.
The second option, Previous captured snapshot , will open a screen with a drop down of existing snapshots in the directory defined when VpK is started. Select the desired snapshot and press the button labeled Connect. The snapshot is parsed and the UI is updated with the information.
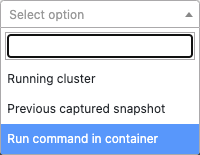
Drop-down when running VpK from a container
When running VpK from a container the drop has three options as shown below. The first two options are the same as above. The third option Run command in container provides the ability to enter a command and have the command run inside the running VpK container. The command output is then displayed in the field below the command input.
Note
The first-time usage of VpK will have no existing snapshots. The "Running cluster" option must be selected to create a new snapshot.
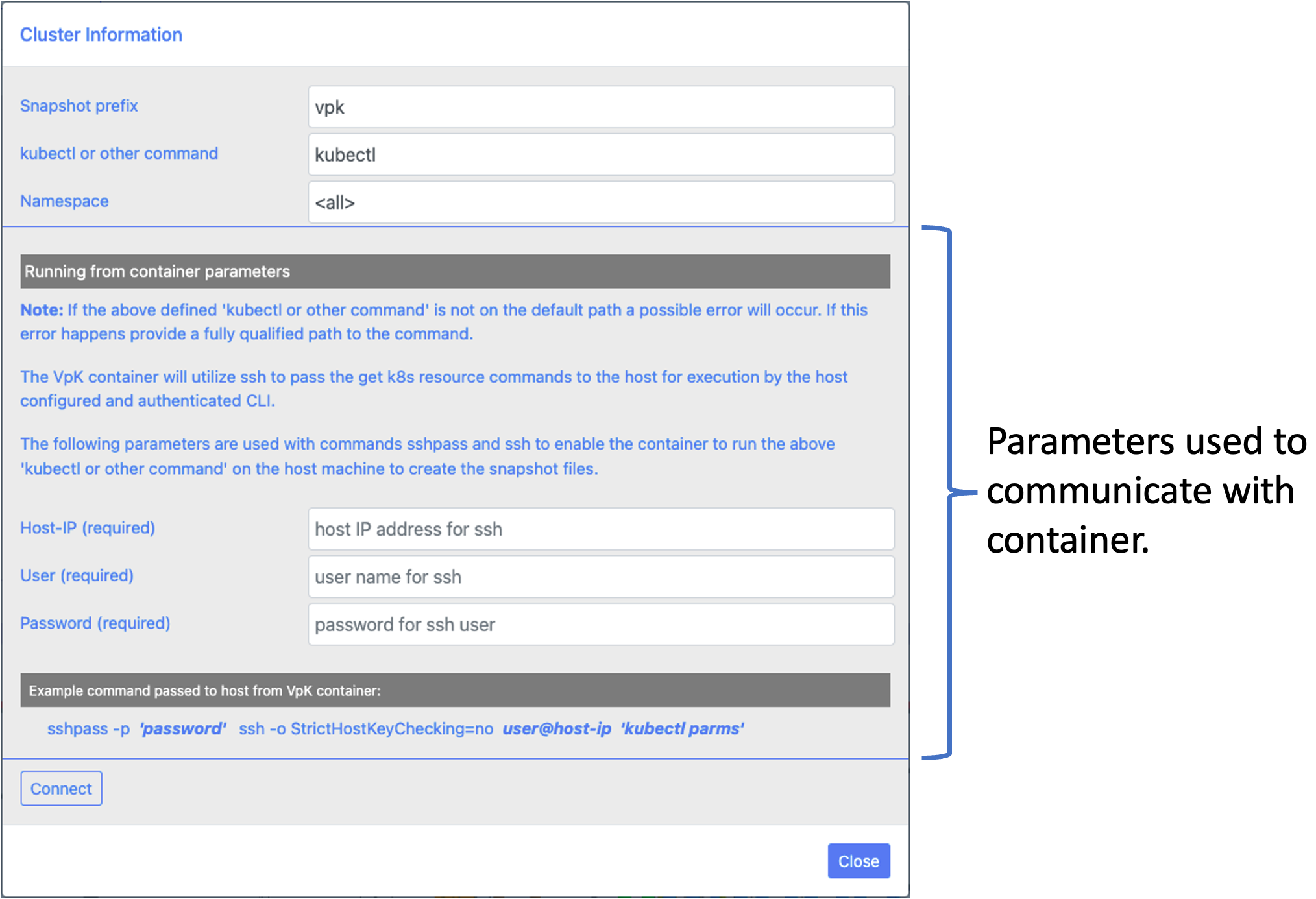
Once an option is selected provide the information to connect to the Kubernetes cluster. Input fields are:
| Field | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Snapshot prefix | This value is appended to the directory name that is created to store the snapshot. | vpk |
| kubectl or other command | The command that is used to communicate with the K8s cluster. | kubectl |
| Namespace | A single namespace or the value |
<all> |
If VpK is started with the '-c' parameter to indicate the application is running from a Docker container three additional fields will be shown. These fields are used to enable the container the ability to run commands on the host machine. This is accomplished using the sshpass and ssh commands. The host machine must have ssh enabled for this feature to successfully work.
| SSH Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Host-IP | IP address of the host machine where the Docker container has been started. |
| User | An existing user on the host machine that is allowed to execute the 'kubectl' or other command. |
| Password | The password of the user that is provided. |
Example sshpass and ssh command
sshpass -p 'password' ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no user@host-ip 'kubectl (along with parameters)'
The dashed outlined section shown below is only shown if VpK is run from a container.
Once the information is provided press the "Connect" button to begin retrieving the K8s data. The cluster snapshot is created and stored in a local directory. The base location for all snapshots is a directory named cluster within the same location where the software is installed. A new snapshot directory within the base 'cluster' directory is created for each new snapshot. The new snapshot directory will use the value provided in the "Snapshot prefix" field along with date and time appended.
Example snapshot directory name that will be created:
vpk-2022-10-26-14h-16m-46s
Connected to k8s
While querying the connected Kubernetes cluster a series of processing messages will be displayed in the bottom portion of the above screen. Returning to the main screen requires closing this screen by pressing the "Close" button.
Snapshot that is connected
Once returned to the home screen of VpK the selected snapshot is shown in the upper portion of the screen. The snapshot name shown is also a button that can be pressed to view statistics. Statistics for the connected snapshot are provided in either a tree map graph or in a table view with a count for each resource kind within the cluster or count of resource kinds within a namespace.
Refer to the Stats tab for more information regarding the statistics.
